Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
Quick Search for Bearing Sizes
OR
Download Ball Bearing Size Chart Catalog
*ISK bearing precision conforms to internationally recognized standards: ABEC、ISO 492, DIN 620, and JIS B1514.
| Bearing No. | Bore(d) (mm) | Outer(D) (mm) | Width(B) (mm) | r (mm) | Dynamic (kgf) | Static (kgf) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6000 | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.5 | 360 | 196 | 19 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.5 | 400 | 229 | 22 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.5 | 440 | 263 | 30 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.5 | 470 | 296 | 39 |
| 6004 | 20 | 42 | 12 | 1 | 735 | 465 | 69 |
| 6005 | 25 | 47 | 12 | 1 | 790 | 525 | 80 |
| 6006 | 30 | 55 | 13 | 1.5 | 1030 | 740 | 116 |
| 6007 | 35 | 62 | 14 | 1.5 | 1250 | 915 | 155 |
| 6008 | 40 | 68 | 15 | 1.5 | 1310 | 1010 | 192 |
| 6009 | 45 | 75 | 16 | 1.5 | 1640 | 1320 | 245 |
| 6010 | 50 | 80 | 16 | 1.5 | 1710 | 1430 | 261 |
* ISK bearing precision conforms to internationally recognized standards: ABEC、ISO 492, DIN 620, and JIS B1514.
| Bearing No. | Bore(d) (mm) | Outer(D) (mm) | Width(B) (mm) | r (mm) | Dynamic (kgf) | Static (kgf) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6200 | 10 | 30 | 9 | 1 | 400 | 229 | 32 |
| 6201 | 12 | 32 | 10 | 1 | 535 | 305 | 37 |
| 6202 | 15 | 35 | 11 | 1 | 600 | 360 | 45 |
| 6203 | 17 | 40 | 12 | 1 | 750 | 460 | 65 |
| 6204 | 20 | 47 | 14 | 1.5 | 1000 | 635 | 106 |
| 6205 | 25 | 52 | 15 | 1.5 | 1100 | 730 | 128 |
| 6206 | 30 | 62 | 16 | 1.5 | 1530 | 1050 | 199 |
| 6207 | 35 | 72 | 17 | 2 | 2010 | 1430 | 288 |
| 6208 | 40 | 80 | 18 | 2 | 2280 | 1650 | 366 |
| 6209 | 45 | 85 | 19 | 2 | 2570 | 1880 | 407 |
| 6210 | 50 | 90 | 20 | 2 | 2750 | 2100 | 463 |
* ISK bearing precision conforms to internationally recognized standards: ABEC、ISO 492, DIN 620, and JIS B1514.
| Bearing No. | Bore(d) (mm) | Outer(D) (mm) | Width(B) (mm) | r (mm) | Dynamic (kgf) | Static (kgf) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 1 | 635 | 365 | 53 |
| 6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 1.5 | 760 | 450 | 60 |
| 6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 1.5 | 895 | 545 | 82 |
| 6303 | 17 | 47 | 14 | 1.5 | 1070 | 660 | 115 |
| 6304 | 20 | 52 | 15 | 2 | 1250 | 785 | 144 |
| 6305 | 25 | 62 | 17 | 2 | 1610 | 1080 | 232 |
| 6306 | 30 | 72 | 19 | 2 | 2090 | 1440 | 346 |
| 6307 | 35 | 80 | 21 | 2.5 | 2620 | 1840 | 457 |
| 6308 | 40 | 90 | 23 | 2.5 | 3200 | 2300 | 633 |
| 6309 | 45 | 100 | 25 | 2.5 | 4150 | 3100 | 833 |
| 6310 | 50 | 110 | 27 | 3 | 4850 | 3650 | 1070 |
* ISK bearing precision conforms to internationally recognized standards: ABEC、ISO 492, DIN 620, and JIS B1514.
| Bearing No. | Bore(d) (mm) | Outer(D) (mm) | Width(B) (mm) | Dynamic (kgf) | Static (kgf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6700 | 10 | 15 | 4 | 103 | 57 |
| 6701 | 12 | 18 | 4 | 109 | 67 |
| 6702 | 15 | 21 | 4 | 117 | 81 |
| 6703 | 17 | 23 | 4 | 122 | 88 |
| 6800 | 10 | 19 | 5 | 135 | 75 |
| 6801 | 12 | 21 | 5 | 150 | 91 |
| 6802 | 15 | 24 | 5 | 163 |
107 |
| 6803 | 17 | 26 | 5 | 206 | 135 |
| 6900 | 10 | 22 | 6 | 212 | 117 |
| 6901 | 12 | 24 | 6 | 227 | 133 |
| 6902 | 15 | 28 | 7 | 340 | 205 |
| 6903 | 17 | 30 | 7 | 360 | 228 |
More thin-section bearing models are available on our website.
* ISK bearing precision conforms to internationally recognized standards: ABEC、ISO 492, DIN 620, and JIS B1514.
| Bearing No. | Bore(d) (mm) | Outer(D) (mm) | Width(B) (mm) | Dynamic (KN) | Static (KN) | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62200 | 10 | 30 | 14 | 5.11 | 2.37 | 44 |
| 62201 | 12 | 32 | 14 | 6.82 | 3.06 | 53 |
| 62202 | 15 | 35 | 14 | 7.64 | 3.72 | 65 |
| 62203 | 17 | 40 | 16 | 9.57 | 4.79 | 96 |
| 62204 | 20 | 47 | 18 | 12.84 | 6.65 | 145 |
| 62205 | 25 | 52 | 18 | 14.02 | 7.88 | 172 |
| 62206 | 30 | 62 | 20 | 19.46 | 11.31 | 275 |
| 62207 | 35 | 72 | 23 | 25.67 | 15.3 | 410 |
| 62208 | 40 | 80 | 23 | 29.52 | 18.14 | 616 |
| 62209 | 45 | 85 | 23 | 31.67 | 20.68 | 625 |
| 62210 | 50 | 90 | 23 | 35.07 | 23.18 | 726 |
The ball bearing size chart is a comprehensive reference guide that displays various dimensions and specifications of ball bearings.
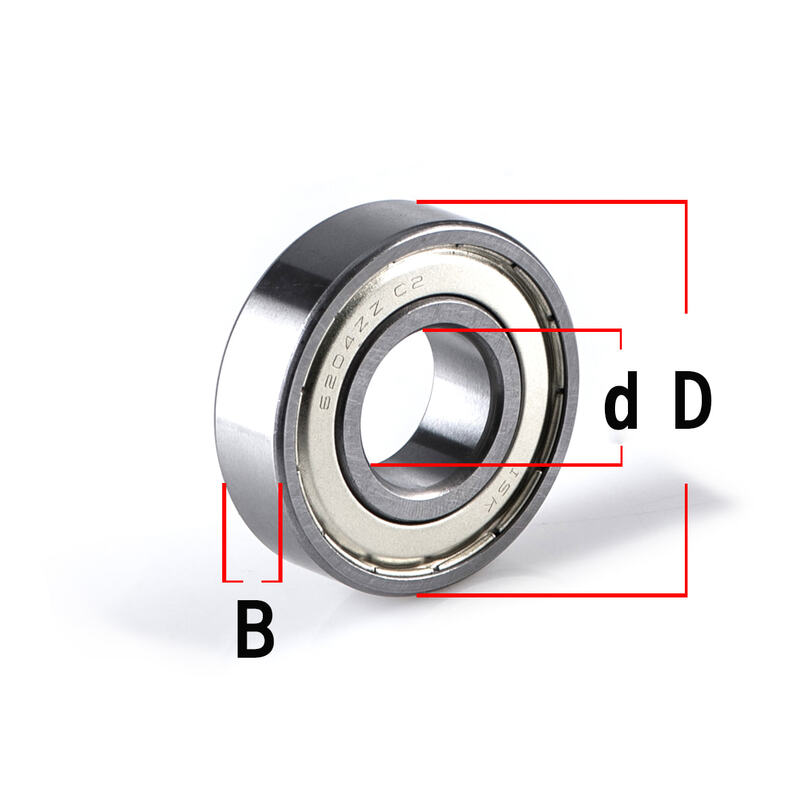
The primary parameters included in a bearing size chart are ID x OD x W.
To measure a ball bearing, you’ll need to find three key dimensions: the bore diameter, outer diameter, and width. These measurements are typically standardized and can be found in the manufacturer's specifications or on the bearing itself. Using tools like calipers or micrometers, you can take precise measurements and use a size chart to choose the right bearing for your needs.
To measure ball bearings, use a vernier caliper to provide accurate measurements. If this tool is not available, measurements can be taken using a ruler.
Follow these steps:
Measure the inner diameter by inserting the outside anvils of the caliper into the inner ring of the bearing.Alternatively, measure the inner circle of the bearing from end to end with a ruler.
Measure the outer diameter by placing the bearing in the jaws of the caliper or measuring the bearing from one outside edge to the other using a ruler.
Repeat the last step for the width of the bearing.
Use a bearing sizes chart to find the bearing series number.
Ball bearings are simple but crucial parts used in many types of machines. They help things spin smoothly, reducing friction and wear. A ball bearing consists of two rings and a set of balls in between. To pick the right one for your machine, a ball bearing size chart is super helpful. It ensures that the bearing you choose works well with your equipment and lasts a long time.
In this article, we will explore the significance of the common ball bearing size chart and understand how to interpret and utilize it effectively.
The common standard ball bearing sizes vary widely based on the type and application of the bearing. Ball bearings are available in both metric and imperial sizes.
The size of a ball bearing is defined by its outer geometry, including:
To measure these dimensions accurately, tools like calipers or micrometers are used. Once measured, you can match the dimensions with a size chart to select the right bearing.
Ball bearings are subjected to radial and axial loads during operation. Load ratings in the size chart indicate the maximum load capacity a bearing can handle before experiencing premature failure.

Axial bearings are made to handle forces that push or pull along their axis. They’re great for supporting axial loads while keeping things running smoothly by reducing friction.

Radial bearings are some of the most common types of rolling bearings, designed to handle loads that act perpendicular to the axis. They provide stable support, reduce friction, and ensure smooth operation under radial loads.
Speed ratings define the maximum rotational speed at which a bearings can operate without causing excessive heat generation or premature wear.
Bearings clearance is the internal gap between the balls and raceways. It influences the bearing's axial and radial play and thermal expansion characteristics.
If a ball bearing is not selected according to the size chart or the specific requirements of the application, several problems can occur:
Using the wrong bearing sizes can lead to misalignment and excessive friction between the bearing and its housing. This extra friction accelerates wear, shortens the bearing's lifespan, and can cause premature failure.
A bearing that’s either too small or too large for the job won’t distribute loads evenly. This imbalance can make the bearing less effective at handling forces and rotations, reducing machinery efficiency and overall performance.
When a bearing isn’t the right size, it may struggle to dissipate heat properly. Friction increases, leading to heat buildup that can degrade lubricants, weaken materials, and eventually cause the bearing to fail.
Using the wrong size bearing can lead to noticeable vibrations and noise during operation. These vibrations not only disrupt smooth performance but can also cause long-term structural damage. Noise is often an early warning sign of misalignment or uneven load distribution, indicating potential issues with the bearing's fit or performance.
Why is my bearing suddenly making noise ? 
Improperly sized bearings are more likely to fail prematurely. Replacing them—and dealing with the cascading problems they cause—can result in expensive downtime, disrupting operations and impacting both productivity and profitability.
In high-stakes applications like automotive or aerospace systems, mismatched bearings can create serious safety hazards. Sudden bearing failure in high-speed or heavy-load scenarios can lead to accidents, risking both equipment integrity and human safety.
To prevent these issues, always refer to the manufacturer's specifications and size charts when choosing bearings for your application. Selecting the right bearing ensures your machinery operates smoothly, lasts longer, and remains safe and reliable.
Understanding the bearing size chart is crucial to making the right selection for your application.
.webp)
Figure out what your application needs to handle—think about the load, speed, temperature, and working environment

Choose the right bearing type from the chart based on what your application requires.
.webp)
Make sure the bearing's dimensions match your shaft and housing needs. The bore diameter, outer diameter, and width should fit your machinery's specifications.
Ensure that the chosen bearing can handle the expected loads and speeds within your application.
Bearing clearance and tolerance may impact the overall system's performance, so make sure they are suitable for your specific needs.
Advantages of ISK BEARINGS Factory 
Choosing the right bearings is key to ensuring reliability and performance. As a leading bearing supplier from Taiwan, we understand how important this is. Our website offers detailed information to help engineers and professionals make well-informed decisions and fully benefit from these valuable resources.
We are delighted to offer you professional consulting services. We firmly believe that choosing the right bearings is an indispensable step in building reliable and efficient machinery. Therefore, we are committed to becoming your most trustworthy partner. Whether you require standardized bearings, custom solutions, or bearings designed for high loads and speeds.
 Extended reading:
Extended reading:
1. Needle Bearing Size Chart|Teach you how to choose bearings correctly
2. Creating a Green Footprint: ISK BEARINGS Corporate Responsibility and ESG Innovation
3. Sleeve Bearing vs Bushing: What Difference Between Them
Bearing model numbers consist of three parts:
We previously helped an electromechanical equipment manufacturer in Asia resolve abnormal bearing noise issues. By optimizing the sealing structure and adjusting lubrication parameters, we significantly improved system stability and reduced maintenance costs.
Case reference: ISK BEARING Customer Cases
We offer a range of testing and technical services, including independent heat treatment, automated noise & vibration testing, clearance inspection, salt spray testing, and more — helping our clients improve product reliability and performance.
Resource overview: ISK Technical Resources
You can visit the ISK official FAQ section to explore answers related to bearing selection, product specifications, and more.
FAQ Section: ISK Bearings FAQ Center
Why is ISK BEARINGS frequently chosen as the specified bearing brand by major international companies?
As a bearing manufacturers, we have established an IATF16949-certified factory in Ningbo to ensure the highest quality of our products, which comply with RoHS, REACH, and SGS standards.
Discover more about the features and applications of various bearings.
Click here to explore more articles and find the perfect bearing for your project.
Needle Bearings (Roller Bearings) are a type of bearing that performs exceptionally well at high speeds. Their rollers are precisely guided by specially shaped, high-rigidity cages with minimal dimensional error. Despite their small cross-section, needle bearings...
How Do Ball Bearings Work? Bearings are often small and unassuming components in a product, yet they are crucial for its proper functioning. Without bearings, many products would fail to operate effectively. But do you know how ball bearings...
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.