Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
ISK Bearings | B2B Bearing Wholesale
Table of Content
- What is a sleeve bearings and bushings?
- What is a Different Types of Bush Bearings?
- Difference Between Bearings and Sleeve Bearings?
- Exploring Sleeve Bearings: Characteristics and Types
- Three Types of Sleeve Bearing
- Exploring Material Versatility in Sleeve Bearing Manufacturing
- What Are Sleeve Bearings Key Features?
Sleeve bearings and bushings are essential components found in various applications, including machinery and equipment. Understanding the differences between these two types of bearings is crucial to make informed decisions regarding their use. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics and applications of sleeve bearings and bushings, shedding light on their functionality, materials, and key features. Join us as we explore the world of sleeve bearings and bushings and their importance in ensuring optimal performance and durability.
 Learn More:What is a Bushing?
Learn More:What is a Bushing?
Bushings, also known as plain bearings or sleeve bearings, come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Here are some common types of bushings:


Bearings are crucial mechanical components that enable smooth motion in various machinery. They come in diverse types, each designed for specific applications. This chapter explores the different types of bearings, their characteristics, and their applications in the industrial and automotive sectors.
Ball bearings are the most common type, utilizing balls to maintain separation between the bearing races. They handle both radial and thrust loads, making them versatile for many applications, from conveyor systems to deep groove ball bearings in household appliances.
Needle bearings are a variation of roller bearings with long, thin rollers. They have a high length-to-diameter ratio, making them suitable for applications with limited radial space, such as in automotive engines and aerospace components.
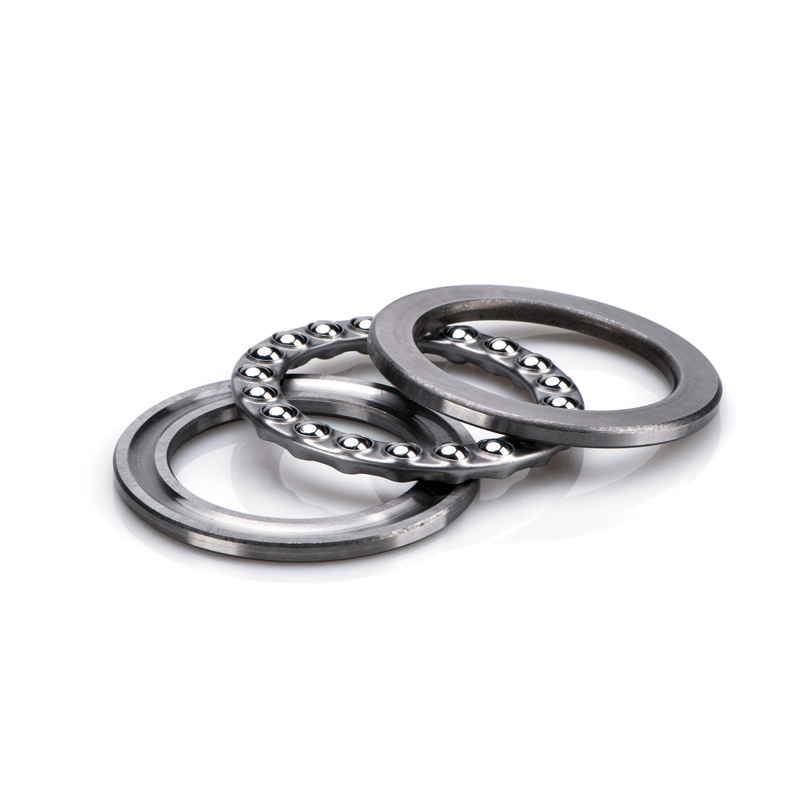

Thrust bearings are designed to handle axial loads, ensuring machinery components can withstand force in one direction. They are prevalent in applications like gearboxes, where axial forces need to be managed efficiently.
.jpg)
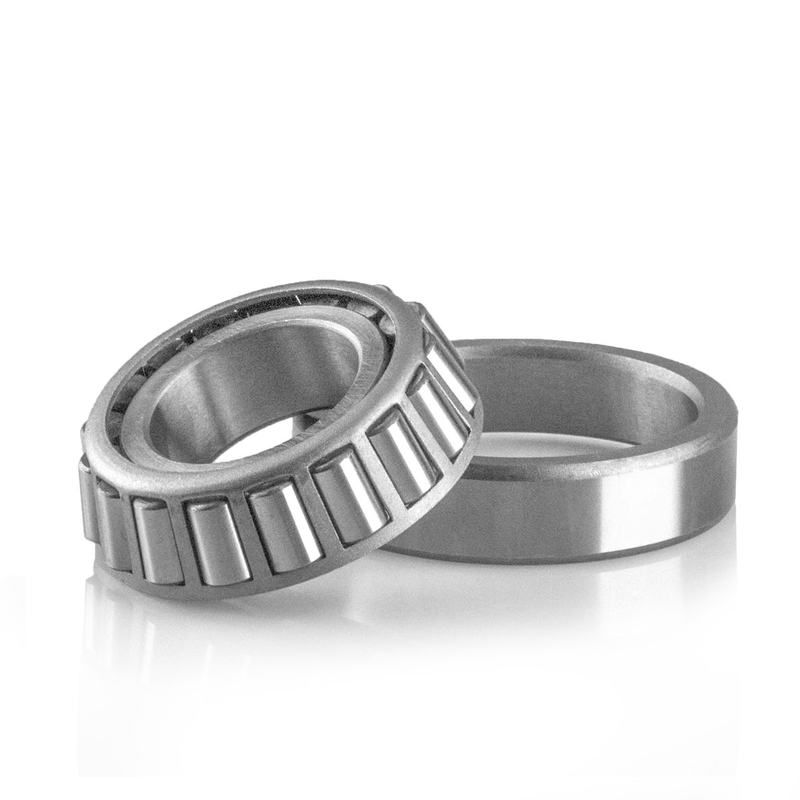
Tapered roller bearings handle both radial and axial loads by employing tapered rollers. They are commonly used in car wheels, ensuring smooth rotation and load-bearing capacity.
.jpg)
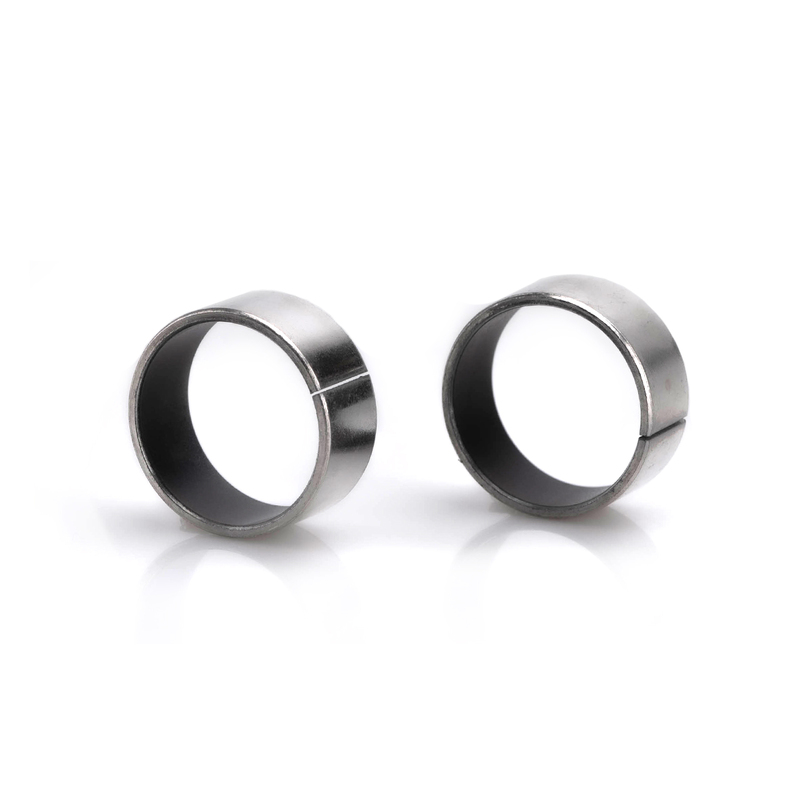
Bushings, also known as sleeve bearings, provide a sliding surface with no rolling elements. They are self-lubricating and are used in applications where low friction and simple design are essential, like in hinges and pivots.
Sleeve bearings, also known as bushings, are essential components used to enable smooth movement and reduce friction in various applications.
.jpg)

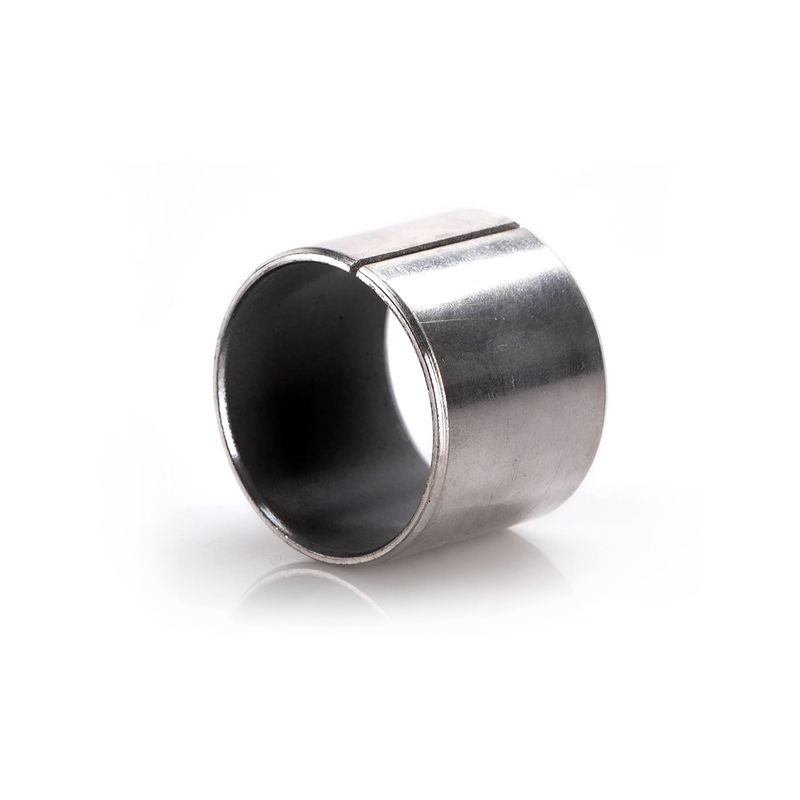
Sleeve bearings are versatile components that play a crucial role in various industries, enabling smooth movement, reducing friction, and enhancing overall performance and durability.
 Save time and quickly find the bearing model and size you need. Inquire now.
Save time and quickly find the bearing model and size you need. Inquire now.
The three types of sleeve bearings—sleeve, flanged, and thrust washer—differ in their designs and applications. Sleeve bearings have a cylindrical shape with straight diameters and are versatile for general use. Flanged plain bearings, resembling sleeve bearings, feature a flange for precise axial location and may include mounting holes for stability. On the other hand, thrust washers are dry sliding components designed for scenarios with limited axial space, challenging maintenance conditions, and the risk of lubricant starvation. Each type serves specific purposes in diverse applications, catering to varying needs in the realm of bearing technology.

A flanged plain bearing has a flange at one end that is used as a locating surface during assembly.
Some flanges may be large enough to incorporate mounting holes used to secure the bearing in place.

Dry sliding thrust washers are designed for applications where axial space is limited, maintenance is not possible, and where lubricant starvation can occur.
Bushings offer suitability for various types of movements, including rotation, oscillation, and linear motion. Different bushing appearances serve different functions.
The most prevalent type is the flanged bearing, capable of handling both axial and side loads. In scenarios where higher side loads are present, a combination of a thrust washer and a cylindrical bearing provides a suitable alternative. Alternatively, for purely radial loads, a simple cylindrical bearing is the optimal choice.
Sleeve bearings can be manufactured using various types of materials to meet different application requirements
Oilless Slide Bushing is made of the PTFE composite material, which is a copper-plated steel plate on which a porous layer of tin bronze powder is sintered and a mixture of PTFE and lead is filled into and covered by a porous layer by a rolling process.
It is a boundary lubricating bushes made of the POM composite material, which also has a copper-plated steel plate on which a tin bronze powder is sintered, and modified polyformaldehyde resin (POM) is firmly anchored in the sintered bronze layer. The surface of the covering layer has many pockets to retain lubricating grease.
.jpg)
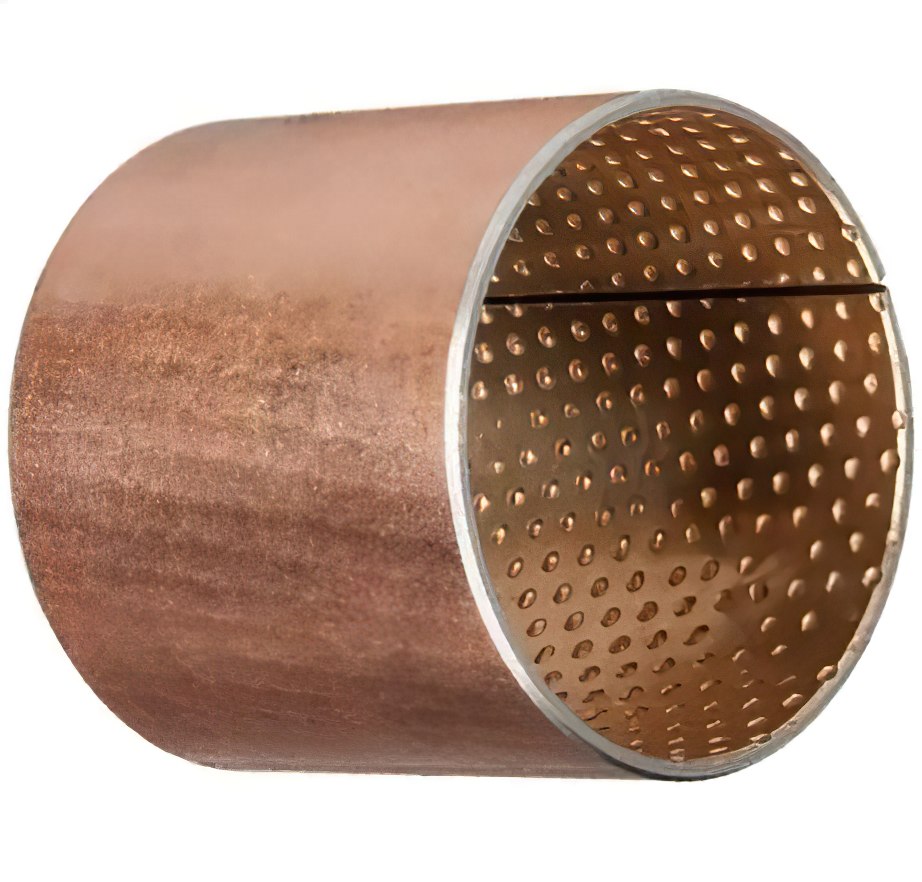
Based on high-quality low carbon steel sintering bronze alloy or lead-free bronze alloy on the surface, provide a high specific load, especially fits for high speed and shock conditions. Oil pockets or grooves can be machined in the liner for better grease storage. Widely used in truck chassis, agricultural machinery, construction machinery, etc. In addition, lead-free meet EU requirements and are the best choice for the automotive field.
The bearing is wrapped in a cold form of able homogenous bronze, which will obtain exceptional material properties. Standard bearings are equipped with diamond-shaped lubrication grooves on the bearing surface. These indentations act as lubricant reservoirs and rapidly form a lubricating film during the start-up motion, reducing start-up friction. Typical applications are widely used in construction machineries such as hoisting machinery, automobiles, tractors, trucks, machine tools, and some mining engines.
This type of bearings material provides a maintenance-free and low-friction bearing especially suitable for high loads and intermittent oscillating motion. Solid lubricants in bronze combine the strength of bronze with the wear resistance of graphite. Applications are used in automotive production lines, water industry, dam gates, plastic molding machinery, etc.
Bronze liners, steel liners or wear plates are abrasion-resistant liners used to decrease wear and tear on surfaces subjected to heavy rolling friction and impact in the machines. In addition, the bronze liners and steel liners have the ultimate objective to help keep the roll center lines precisely where they should be. Two very popular bronze alloys used for wear plate bearing pads are C93200 SAE 660 Bearing Bronze and C95400 Aluminum Bronze. Bronze liners are used on multiple wear surfaces throughout a rolling mill. The goal of the bronze liners is to assist in keeping the roll center lines at precisely the desired locations. Bronze liners and wear plates play a very important role in multiple locations on today’s metal rolling equipment. Using poorly designed liners or liners that are not compatible with the surfaces they contact can greatly reduce product quality and increase maintenance expense.
Bearing model numbers consist of three parts:
We previously helped an electromechanical equipment manufacturer in Asia resolve abnormal bearing noise issues. By optimizing the sealing structure and adjusting lubrication parameters, we significantly improved system stability and reduced maintenance costs.
Case reference: ISK BEARING Customer Cases
We offer a range of testing and technical services, including independent heat treatment, automated noise & vibration testing, clearance inspection, salt spray testing, and more — helping our clients improve product reliability and performance.
Resource overview: ISK Technical Resources
You can visit the ISK official FAQ section to explore answers related to bearing selection, product specifications, and more.
FAQ Section: ISK Bearings FAQ Center
Discover more about the features and applications of various bearings.
Click here to explore more articles and find the perfect bearing for your project.
Needle Bearings (Roller Bearings) are a type of bearing that performs exceptionally well at high speeds. Their rollers are precisely guided by specially shaped, high-rigidity cages with minimal dimensional error. Despite their small cross-section, needle bearings...
How Do Ball Bearings Work? Bearings are often small and unassuming components in a product, yet they are crucial for its proper functioning. Without bearings, many products would fail to operate effectively. But do you know how ball bearings...
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.