Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
⬇️ Scroll Down Now or Contact ISK for More Bearing Information
Table of content
Bearings are common mechanical components used to support and constrain the rotation or movement of shafts or bearing housings. Bearings reduce friction and support weight, making mechanical systems operate more smoothly and efficiently. Bearings come in various specifications.
When selecting and using bearings, understanding their specifications is crucial. Bearing specifications not only affect performance but also directly impact the operational efficiency and lifespan of mechanical equipment.
Bearing model numbers typically consist of letters and numbers, with each character representing a specific meaning.
In general, bearing model numbers are divided into three parts:

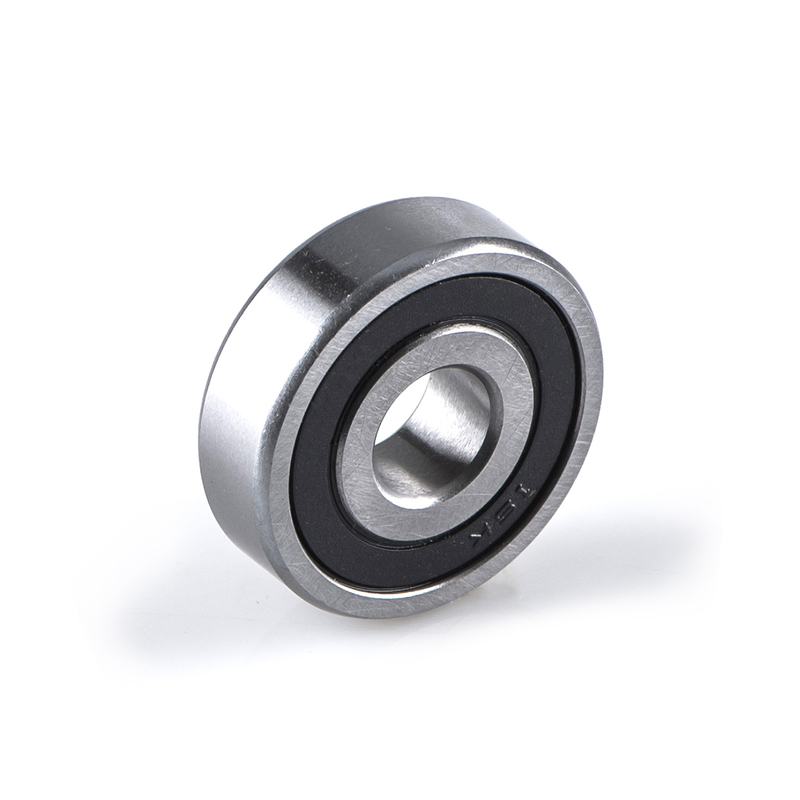
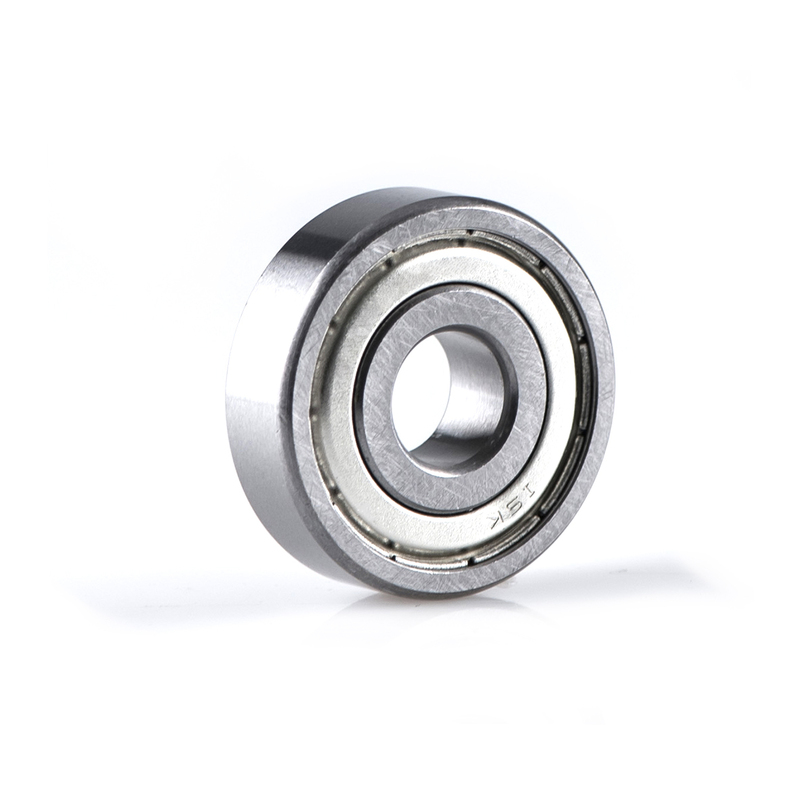
"2RS" indicates double-sided seals. "Z" indicates a single-sided dust cover.
.jpg)
%E4%B8%BB.jpg)
(1) Size and Capacity: The size and capacity of a bearing depend on its design and application requirements. Common dimensions include inner diameter, outer diameter, width, and bearing clearance. Bearing capacity indicates the maximum load it can withstand, usually expressed in terms of dynamic load rating and static load rating.
Unveiling the Mystery of Ball Bearing Sizes 
(2) Materials: Bearings are typically made of metal, such as steel or stainless steel. These materials offer good strength and wear resistance. Additionally, ceramic or plastic materials may be used for special applications.
Unveiling the Mystery of Ball Bearings' Composition: Dive into the Details 
(3) Lubrication: Bearings require lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Common lubrication methods include grease, oil, and solid lubricants.
(4) Preload: Preload is an additional force applied within the bearing to maintain proper contact between internal components. It can be categorized as axial preload and radial preload, depending on the application requirements.
(5) Accuracy Class: The accuracy class of a bearing affects its smooth operation and precision. Common accuracy classes include ABEC (American Bearing Manufacturers Association) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards.
Introduction to Bearings | Basic knowledge 
It is important to note that bearing specifications and characteristics vary depending on the application requirements. Selecting the appropriate bearing specifications is a key factor in ensuring the normal operation and extended lifespan of mechanical systems. Therefore, when choosing bearings, careful consideration should be given to factors such as load, speed, environmental conditions, and other relevant parameters to ensure that the bearings meet the specific application needs.
Common Types of Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearing generally consists of an inner ring, an outer ring, a spherical rolling element and a cage.The orbital ditch is slightly larger than the radius of the steel ball.Due to the point contact between the ball and the track, the deep groove ball bearing can withstand the bidirectional axial load in addition to the radial load.
The miniature bearing is a small-sized deep groove ball bearing. It is a metric series of bearings with an outer diameter of less than 9 mm. The inner diameter is usually 1 mm but it can be as small as 0.6 mm.
The use of small outer diameter steel balls can reduce friction significantly, it is high rigidity and provides good rotational accuracy.
The thin section bearings with large bores and small cross-sections can use the large-diameter hollow shafts to replace small-diameter solid shafts, which use hollow shafts to ensure space for light weight and wiring.
Thrust ball bearings generally consist of two or more thrust washers and several rolling elements. The thrust washers are typically divided into shaft washers and seat washers, and the rolling elements are typically held together by a steel or copper cage.
The rolling elements of this bearing are tapered rollers. They form a line contact with raceway of inner ring and outer ring, that can be separable. They are available in both metric, inch, and non-standard dimensions.
Discover more about the features and applications of various bearings.
Click here to explore more articles and find the perfect bearing for your project.
Needle Bearings (Roller Bearings) are a type of bearing that performs exceptionally well at high speeds. Their rollers are precisely guided by specially shaped, high-rigidity cages with minimal dimensional error. Despite their small cross-section, needle bearings...
How Do Ball Bearings Work? Bearings are often small and unassuming components in a product, yet they are crucial for its proper functioning. Without bearings, many products would fail to operate effectively. But do you know how ball bearings...
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.