Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
ISK Bearings | B2B Bearing Wholesale
Table of Contents
Bearings are mechanical components that reduce friction between moving parts. Common bearing types include:
• Ball bearings - suitable for high-speed, low-to-moderate load applications
• Roller bearings - designed for heavy radial loads
• Needle roller bearings - ideal for space-limited applications
• Thrust ball bearings - handle axial loads in low-speed applications
• Tapered roller bearings - support combined radial and axial loads
• Self-aligning ball bearings - accommodate shaft misalignment
• Cylindrical roller bearings - provide high radial load capacity
• Spherical roller bearings - handle heavy loads with self-aligning capability
Bearings can be categorized by contact type (rolling vs. sliding) or load direction (radial vs. thrust). This guide explains their structures, applications, and selection criteria.
Ball bearings are very common because they can carry radial and axial loads, but only a small amount of weight. They exist in various applications such as roller blades and even hard drives, but if they are overloaded they are easily deformed.
Roller bearings are designed to carry heavy loads - the main rollers are cylindrical, which means the load is distributed over a larger area, allowing the bearing to carry more weight.
However, this construction means that the bearing can withstand mainly radial loads, but is not suitable for thrust loads. For applications where space is an issue, needle roller bearings can be used.
Needle bearings are suitable for small diameter cylinders and are therefore easier to install in smaller applications.
These bearing types are designed to handle thrust loads almost exclusively in low speed low weight applications. For example, bar stools utilize ball thrust bearings to support the seat.
Roller thrust bearings, much like ball thrust bearings, can handle thrust loads. The difference, however, is in the weight the bearing can carry: Roller thrust bearings can support significantly larger amounts of thrust loads, and are therefore found in automotive transmissions, where they are used to support helical gears. Gear supports are generally a common application for roller thrust bearings.
Tapered roller bearings are designed to handle large radial and axial loads - due to their load versatility, they are found in automotive wheel hubs, where wheels are expected to experience extreme radial and thrust loads.
These bearings are designed to accommodate misalignment between the shaft and housing. They have two rows of balls and are capable of self-alignment, reducing the impact of misalignment on the bearing's performance.
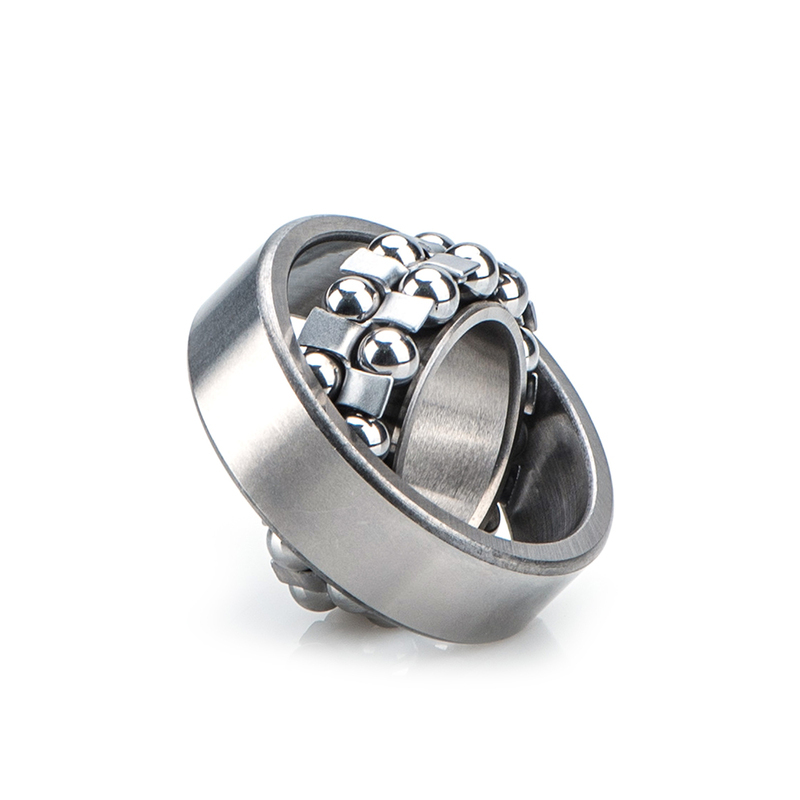

The rollers of cylindrical roller bearings are usually guided by two ribs of a certain ring. The cage, the rollers and the guide ring form a combined part, which can be separated from the other ring, which is a separable bearing. This bearing types is more convenient to install and disassemble, especially when the inner and outer rings are required to have an interference fit with the shaft and the outer casing.
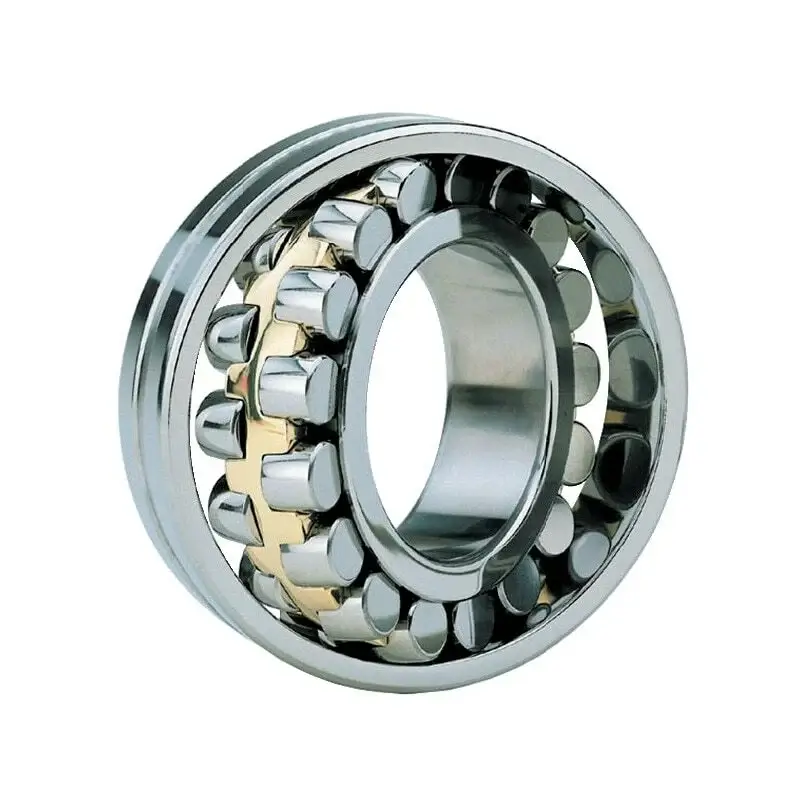
The spherical roller bearing has two rows of rollers, the outer ring is a spherical raceway, and the inner ring has two raceways inclined at a certain angle relative to the bearing axis. The bearings are self-aligning, so they are less susceptible to misalignment between the shaft and the bearing housing and bending or deformation of the shaft. In addition to being able to withstand high radial loads, spherical roller bearings can also withstand axial loads acting in both directions.

A rod end bearing consists of a spherical plain bearing and an eye-shaped body with an integral shank. The spherical plain bearing, typically made of stainless steel or other high-performance materials, is a self-aligning bearing that allows angular misalignment between the shank and the bore. The bearing is often composed of an inner ring with a spherical convex outside diameter and an outer ring with a matching concave inside diameter.
Bearings are mechanical devices that reduce friction between moving parts during rotary or linear motion. They achieve this by replacing sliding friction with rolling friction, significantly improving mechanical efficiency and reducing energy loss.

By minimizing friction, bearings enable smoother rotation and higher operational speeds, improving overall system efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Bearing arrangements include not only rolling bearings, but also bearing-related components such as shafts and housings. Lubricants are also a very important part of the bearing arrangement, as lubricants are required to prevent wear and corrosion so that the bearings can perform their full function.
The seal is also a very important component, and the performance of the seal is critical to the cleaning of the lubricant. Keeping it clean has a profound effect on the life of the bearing.
In order to design a rolling bearing arrangement, it is necessary to select the appropriate bearing type and determine the appropriate bearing size.It’s important to learn types of bearings and their applications.
.webp)
Such as proper form and design of other components in the bearing arrangement, correct fit and internal clearance or preload of the bearing. Fixtures, appropriate seals, type and dosage of lubricant, installation and removal methods, etc.
Each individual decision affects the performance, reliability and economy of the bearing arrangement. The amount of work required depends on having similar bearing selection experience.
In the case of inexperience, special requirements, or special considerations for the cost of bearing arrangements and any other subsequent profiles, more work, such as more precise calculations and/or testing, is required.
Rolling contact bearings use balls or rollers as rolling elements to reduce friction between moving parts. By using rolling motion, these bearings help minimize the friction created between surfaces.
In contrast, sliding contact bearings rely on surface-to-surface sliding. While the argument to convert sliding friction into rolling friction is common, it is considered one-sided as both bearing types serve specific functions in different applications.
Understanding Load Types
Bearings are designed to handle two primary types of loads:
• Radial loads - Forces applied perpendicular to the shaft axis. Example: The weight supported by a wheel bearing during straight-line driving.
• Axial loads (thrust loads) - Forces applied along the axis direction. Example: The lateral forces on a car tire when cornering.
Many bearing designs can handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously, such as ball bearings or tapered roller bearings, with the specific structure optimized based on the primary load direction and magnitude.
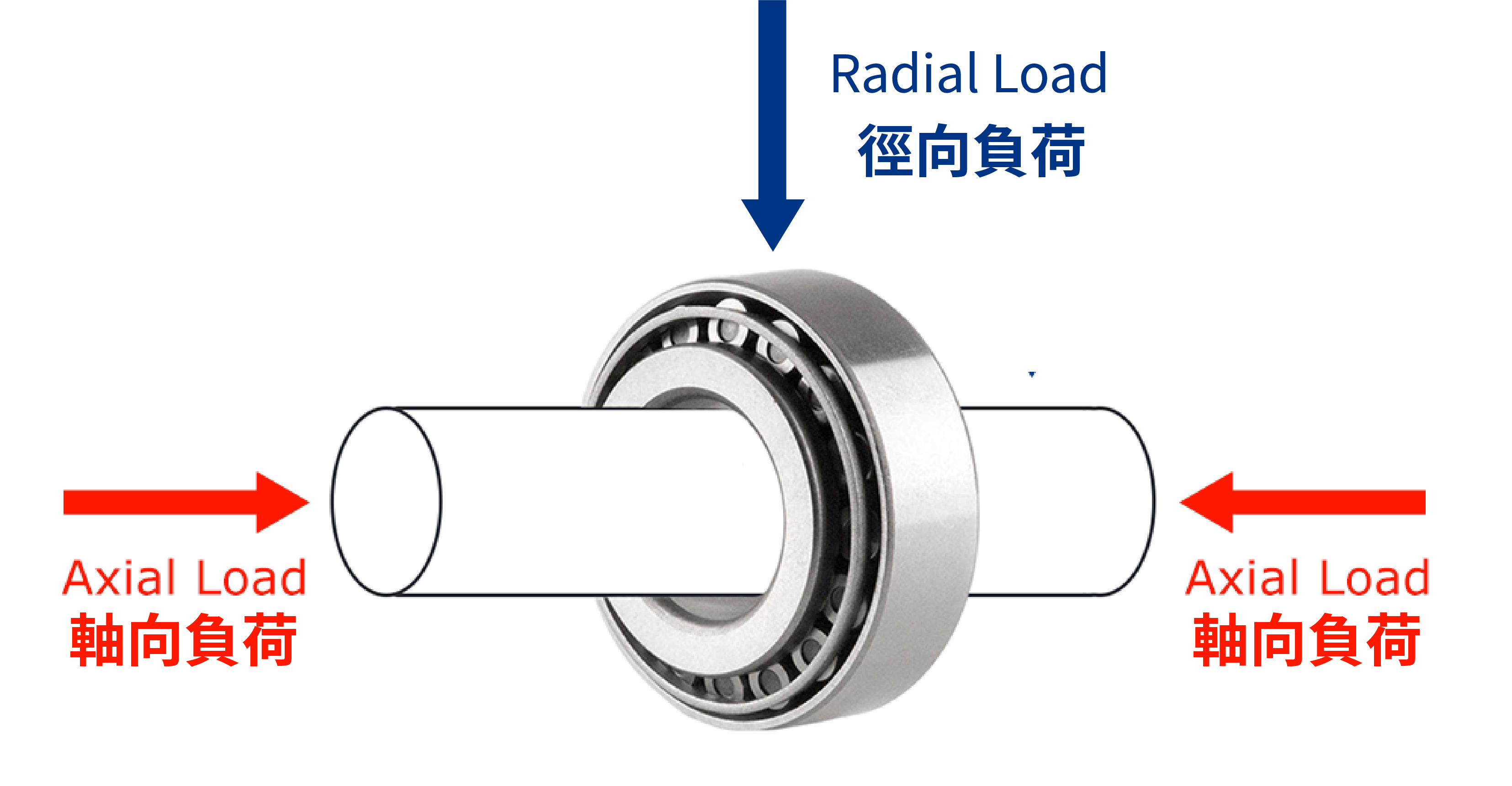

Many bearings are susceptible to radial and axial loads. For example, car tires experience radial loads when driving in a straight line: the tires roll forward in a rotational fashion due to tension and the weight they support. However, when the car rounds a corner, it experiences thrust loads because the tires are no longer just moving in a radial fashion and the cornering forces are heavy on the bearing flanks.
There are many different bearing types designed to handle radial loads, thrust loads or some combination of the two. Since different applications require bearings designed to handle specific loads and different weights, therefore the differences between bearing types relate to the type of load and the ability to handle weight.

Radial bearings are widely used rolling bearings designed primarily to withstand radial loads perpendicular to the axis direction. When loads are applied perpendicular to the axis of the bearing, radial bearings can provide stable support and reduce friction, thereby enabling smooth rotation.

Axial bearings are designed to withstand axial forces, which are forces applied along the axis direction. When loads are applied along the axis of the bearing, it can efficiently provide support and reduce friction, thereby achieving smooth operation.
In the second part of types of bearings and their applications, we’ll be talking about bearing uses. In terms of its function, it should be a support, that is, it is used to bear the shaft in a literal interpretation, but this is only a part of its function. The essence of support is to be able to bear radial loads. It can also be understood that it is used to fix the shaft. Bearing quick and easy automatic selection is included. It is to fix the shaft so that it can only rotate, and control its axial and radial movement.

Because the shaft may move in any direction, and the motor requires that the shaft can only rotate. In theory, it is impossible to achieve the function of transmission. Not only that, the bearing will also affect the transmission.
In order to reduce this effect, good lubrication must be achieved on the bearings of the high-speed shaft. Some bearings have already been lubricated themselves, which are called pre-lubricated bearings. Most bearings must have lubricating oil, which is responsible for not only increasing energy consumption due to friction at high speed, but also terrifyingly easily damaging the bearings. The argument to convert sliding friction into rolling friction is one-sided, because there is something called a sliding bearing.

The purpose of lubricating rolling bearings is to reduce internal friction and wear of the bearing, prevent burning and sticking; prolong its service life; discharge friction heat, cooling, prevent bearing overheating, and prevent the aging of the lubricating oil; effect.
Bearing lubrication methods are divided into grease lubrication and oil lubrication. In order to make the bearing function well, first of all, it is necessary to select a lubrication method suitable for the conditions of use and the purpose of use. If only lubrication is considered, the lubricity of oil lubrication is dominant. However, grease lubrication has the advantage of simplifying the structure around the bearing. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of grease lubrication and oil lubrication.
 When lubricating, pay special attention to the amount, whether it is oil lubrication or grease lubrication, if the amount is too small, the lubrication will not fully affect the bearing life, and if the amount is too large, it will cause large resistance and affect the speed.
When lubricating, pay special attention to the amount, whether it is oil lubrication or grease lubrication, if the amount is too small, the lubrication will not fully affect the bearing life, and if the amount is too large, it will cause large resistance and affect the speed.
The seal of the bearing can be divided into two types: self-contained seal and external seal. The so-called bearing self-sealing is to manufacture the bearing itself into a device with sealing performance.
Such as bearings with dust cover, sealing ring and so on. This kind of seal takes up little space, is easy to install and disassemble, and has a relatively low cost.
The metal dust shields prevent dust and dirt from entering the interior of the bearing while retaining the lubricant within, thereby reducing maintenance requirements. However, this design is not suitable for use in humid or highly dusty environments, as the metal dust shields may not effectively prevent water from entering.
The rubber seals offer excellent dust and water resistance, effectively preventing the ingress of dust, water, and dirt while retaining the lubricant inside the bearing. This design is suitable for use in harsh environments, providing a longer lifespan and requiring less maintenance.
The so-called bearing plus sealing performance device is a sealing device with various performances manufactured inside the installation end cover, etc.
Bearing seals are divided into non-contact seals and contact seals.
 Among them, the non-contact seal is suitable for high-speed and high-temperature occasions, and has different structural forms such as gap type, labyrinth type and gasket type. Contact seals are suitable for medium and low-speed working conditions, and commonly used structural forms such as felt seals and leather cup seals.
Among them, the non-contact seal is suitable for high-speed and high-temperature occasions, and has different structural forms such as gap type, labyrinth type and gasket type. Contact seals are suitable for medium and low-speed working conditions, and commonly used structural forms such as felt seals and leather cup seals.
 Learn More:
Learn More:
Needle Bearing vs Ball Bearing: What's the Difference?
Types of Wheel Bearings: All Need to Know about Wheel Bearing
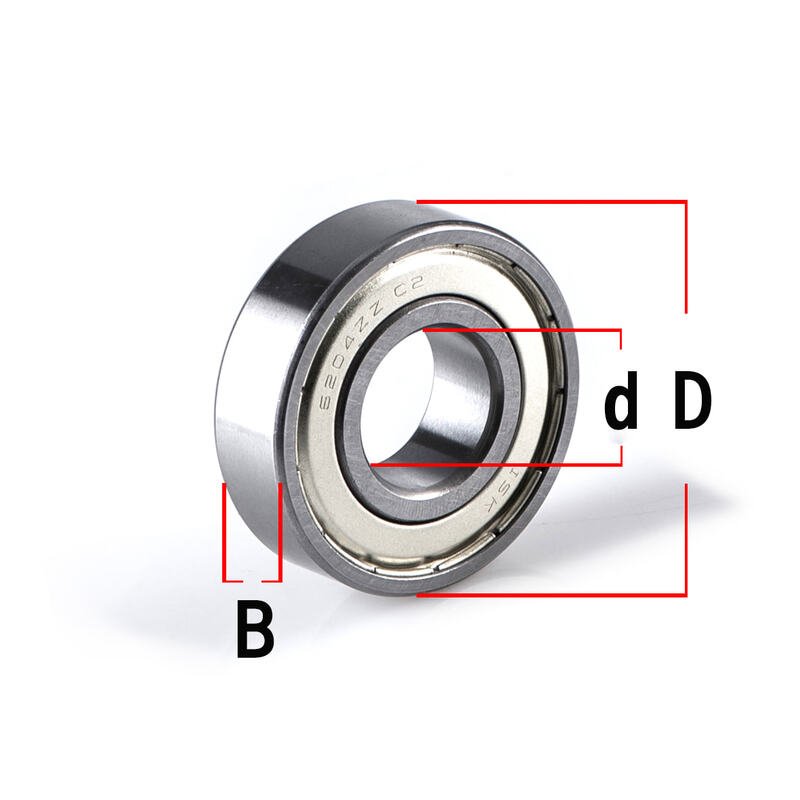
Bearing model numbers consist of three parts:
We previously helped an electromechanical equipment manufacturer in Asia resolve abnormal bearing noise issues. By optimizing the sealing structure and adjusting lubrication parameters, we significantly improved system stability and reduced maintenance costs.
Case reference: ISK BEARING Customer Cases
We offer a range of testing and technical services, including independent heat treatment, automated noise & vibration testing, clearance inspection, salt spray testing, and more — helping our clients improve product reliability and performance.
Resource overview: ISK Technical Resources
You can visit the ISK official FAQ section to explore answers related to bearing selection, product specifications, and more.
FAQ Section: ISK Bearings FAQ Center
Discover more about the features and applications of various bearings.
Click here to explore more articles and find the perfect bearing for your project.
Needle Bearings (Roller Bearings) are a type of bearing that performs exceptionally well at high speeds. Their rollers are precisely guided by specially shaped, high-rigidity cages with minimal dimensional error. Despite their small cross-section, needle bearings...
How Do Ball Bearings Work? Bearings are often small and unassuming components in a product, yet they are crucial for its proper functioning. Without bearings, many products would fail to operate effectively. But do you know how ball bearings...
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.