Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
Table of content
Spherical bearings, also known as ball joint bearings, are designed to rotate and tilt in multiple axes. This flexibility allows them to compensate for angular misalignment between shafts while ensuring smooth transmission. They are commonly used in transmission systems, including automotive suspension, steering systems, and various mechanical equipment that require axial flexibility.
An inner bearing and an outer casing. The inner bearing is usually spherical in shape with a ball-crown structure to accommodate and support the ends of the shafts. The outer casing is a structure with a spherical groove that secures the inner bearing and provides mounting and connection points.
SPHERICAL BEARINGS SPECIFICATION TABLE 
In summary, a spherical bearing is designed to connect two non-concentric shafts in transmission systems. It compensates for angular misalignment while handling axial loads and lateral forces.
 Further Reading:
Further Reading:
Rod End Bearings: Key to Mechanical Connections
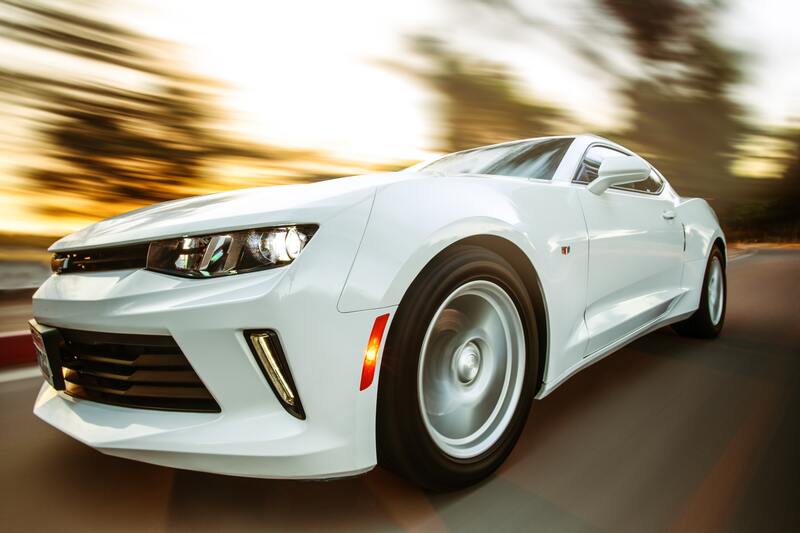

Spherical bearings are commonly used in automotive suspension systems and steering systems. They are used to connect the wheels and suspension system, allowing the wheels to rotate freely and adapt to uneven road surfaces.
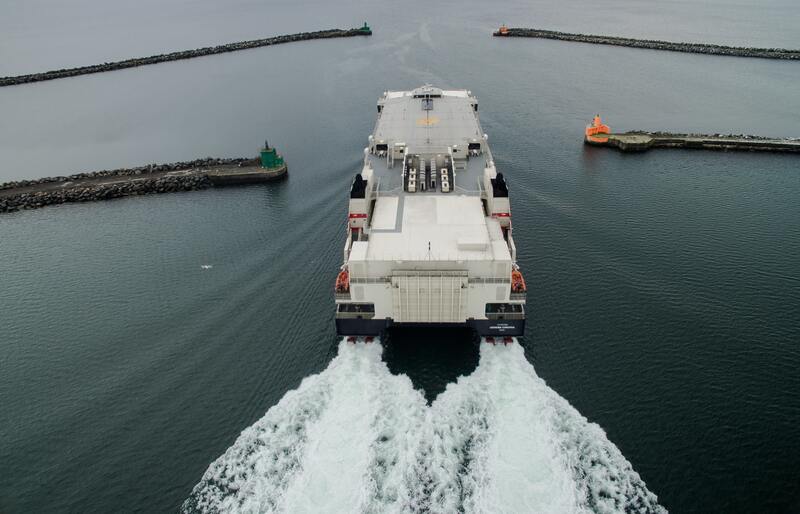

In the marine sector, spherical bearings are used to connect propeller shafts and engines, enabling the propellers to rotate and change direction as needed.
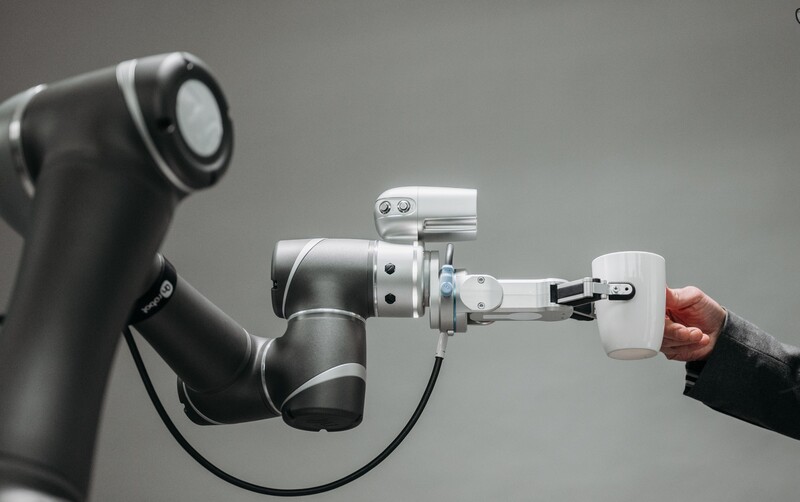

Spherical bearings are frequently employed in the joint components of robots. These bearings enable the robot's arms and joints to move in multiple axes.
Spherical bearings are used in many industries because they can handle angular misalignment, making them essential in a wide range of mechanical systems. These are just a few examples of their versatility.
|
Bearing No. |
Bore(d)(mm) |
Outer(D)(mm) |
Width(B)(mm) |
Weight(g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE4E | 4 | 12 | 3 | 3.3 |
| GE5E | 5 | 14 | 4 | 3.8 |
| GE6E | 6 | 14 | 4 | 4.2 |
| GE8E | 8 | 16 | 5 | 7.5 |
| GE10E | 10 | 19 | 6 | 11 |
| GE12E | 12 | 22 | 7 | 17 |
| GE15E | 15 | 26 | 9 | 32 |
| GE17ES | 17 | 30 | 10 | 49 |
| GE20ES | 20 | 35 | 12 | 65 |
| GE25ES | 25 | 42 | 16 | 115 |
| GE30ES | 30 | 47 | 18 | 160 |
| GE35ES | 35 | 55 | 20 | 258 |
| GE40ES | 40 | 62 | 22 | 315 |
| GE45ES | 45 | 68 | 25 | 413 |
| GE50ES | 50 | 75 | 28 | 560 |
 If you would like to learn more about the specifications of rod end bearings, please refer to the「Rod End Bearing Series Specifications
If you would like to learn more about the specifications of rod end bearings, please refer to the「Rod End Bearing Series Specifications 」 for further information.
」 for further information.
Want to know about other bearing series
 Read more about Needle Roller Bearings Series: What Are Needle Bearings? What is needle bearing used for?
Read more about Needle Roller Bearings Series: What Are Needle Bearings? What is needle bearing used for?
 Read more about Ball Bearings Series: How Ball Bearing Works? Tell You the Operating Principle
Read more about Ball Bearings Series: How Ball Bearing Works? Tell You the Operating Principle
 Read more about Bushes Series: Difference Between Bushing and Bearing: Major Differences
Read more about Bushes Series: Difference Between Bushing and Bearing: Major Differences
Discover more about the features and applications of various bearings.
Click here to explore more articles and find the perfect bearing for your project.
Needle Bearings (Roller Bearings) are a type of bearing that performs exceptionally well at high speeds. Their rollers are precisely guided by specially shaped, high-rigidity cages with minimal dimensional error. Despite their small cross-section, needle bearings...
How Do Ball Bearings Work? Bearings are often small and unassuming components in a product, yet they are crucial for its proper functioning. Without bearings, many products would fail to operate effectively. But do you know how ball bearings...
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.