Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
Table of content
Bearings are essential components used in various machinery and equipment to reduce friction and enable smooth rotational or linear motion. They support loads and facilitate the transfer of forces between moving parts. With a wide range of applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and more, understanding the different types of bearings is crucial. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of various bearing types, their construction, functions, and applications.
Roller bearings use cylindrical rollers for heavy loads, while ball bearings use spherical balls for lighter loads and high speeds.
Roller bearings use cylindrical rollers instead of balls to distribute the load. These rollers are longer than balls and have a larger contact area with the inner and outer races. Roller bearings are capable of handling heavier loads and are often used in applications with radial loads, such as conveyor belt rollers and heavy machinery.
 View Bearing Type -Needle Roller Bearings
View Bearing Type -Needle Roller Bearings
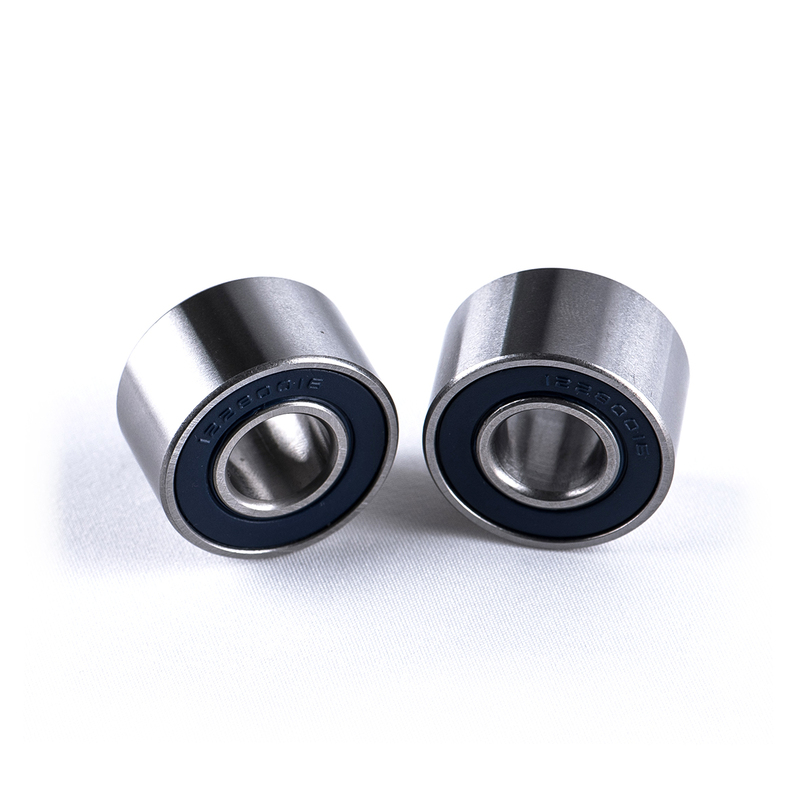
Ball bearings use spherical balls to maintain separation between the bearing races. They are suitable for both radial and thrust loads and are commonly used in high-speed applications where low friction is essential. Ball bearings are found in various devices, including electric motors, automotive wheels, and household appliances.
 View Bearing Type - Ball Bearings
View Bearing Type - Ball Bearings
 View Bearing Type - Ball Bearings
View Bearing Type - Ball BearingsThe advantages of ball bearings are multifaceted. They exhibit exceptional wear resistance, demand minimal lubrication, incur low friction, resulting in minimal energy loss, boast an impressive service life, and offer ease of replacement, all while maintaining compact dimensions. Additionally, they are relatively economical and can adeptly handle thrust loads.
Need Assistance Selecting The Proper Bearings?
If you need help selecting the best products for your specific industry application, ISK BEARINGS offers application support as part of our value-added services to make your job easier.
 View Bearing Type - Deeep Groove Ball Bearings
View Bearing Type - Deeep Groove Ball Bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are widely used in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, electrical, aviation, and transportation. They provide support, reduce friction, and ensure smooth motion in critical components such as engines, transmission systems, machine tools, electric motors, and more. Their versatility and widespread application make them essential in the industrial sector.
Inner Diameter (d):
The inner diameter refers to the size of the central hole or bore of the bearing.
Outer Diameter (D):
The outer diameter is the measurement of the bearing's outer ring.
Width (B):
The width, also known as the thickness, refers to the dimension between the inner and outer rings of the bearing.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
|
(1). Versatility |
Deep groove ball bearings can accommodate both radial and axial loads, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. |
|
(2). Low Friction |
They have very low rolling friction, ensuring efficient and smooth operation, especially in high-speed applications. |
|
(3). Long Service Life |
When properly maintained, deep groove ball bearings have a long operational lifespan, contributing to cost-effectiveness. |
|
(4). Easy Installation |
They are comparatively easy to install, simplifying the assembly process and reducing downtime. |
|
(5). Minimal Maintenance |
Deep groove ball bearings require minimal maintenance, leading to lower maintenance costs and increased operational efficiency. |
|
(6). Cost-Effectiveness |
They offer a balance between performance and cost, providing excellent value for the investment. |
|
(7). Availability |
Deep groove ball bearings are widely available in the market. |
When selecting a bearing, it's crucial to consider these dimensions in relation to your application requirements. Factors such as the magnitude and direction of the load, operating speed, temperature, and desired service life should also be taken into account.
.jpg)
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
|
(1). High Axial Load Capacity |
Angular contact roller bearings are designed to withstand greater two-way axial loads, making them suitable for applications where both radial and axial loads need to be supported simultaneously. |
|
(2). Versatility in Load Handling |
These bearings can handle both radial and axial loads efficiently, providing versatility in various industrial applications. |
|
(3). Axial Load Transfer |
Due to the displacement of the inner and outer rings, the axial load can be transferred to the housing through the bearing. This feature ensures effective load distribution and stability in machinery. |
|
(4). Rigid Axial Guidance |
Angular contact bearings are ideal for applications where rigid axial guidance is necessary, ensuring precise and controlled movement in machinery. |
|
(5). Enhanced Durability |
The ability to handle significant axial loads contributes to the durability and longevity of angular contact bearings, making them reliable components in heavy-duty applications. |
|
(6). Increased Load Capacity |
Their capability to withstand both radial and axial loads increases the overall load-carrying capacity of the bearing, allowing for efficient performance under challenging conditions. |
Angular contact ball bearings have diverse applications in industries such as machine tools, automotive, aerospace, industrial gearboxes, electric motors, robotics, pumps, compressors, and agriculture. They provide precision, support radial and axial loads, and ensure reliable operation in these sectors.
 View Bearing Type -Thrust Ball Bearings
View Bearing Type -Thrust Ball BearingsThrust ball bearings are widely used in various industries to support axial loads. They are essential components in automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery, and power generation applications. In the automotive sector, they are found in transmissions, steering systems, and drive shafts. Aerospace applications include control surfaces, landing gear systems, and thrust reversers. Heavy machinery, such as cranes and excavators, relies on thrust ball bearings for efficient load handling. Similarly, power generation equipment like turbines and pumps utilize these bearings to support axial loads. The versatility and reliability of thrust ball bearings make them indispensable in industries requiring precise axial load management.
Inner Diameter (d, d1):
The inner race contains the groove where the rolling elements (balls) are located.
Outer Diameter (D1, D):
The outer diameter of a thrust ball bearing refers to the measurement of the outside diameter of the outer race.
Width (T):
The width of a thrust ball bearing, also known as the axial height or thickness, refers to the measurement of the distance between the two races. It includes the rolling elements (balls) and represents the dimension in the axial direction.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
|
(1). Low Noise and Smooth Operation |
Thrust ball bearings operate with minimal noise and ensure smooth functioning, enhancing the overall performance of the machinery. |
|
(2). Adaptability to High-Speed Applications |
These bearings can be adapted to high-speed applications, providing reliable performance even in demanding, fast-paced environments. |
|
(3). One-Way or Two-Way Usage |
They can be used as one-way or two-way bearings, allowing flexibility in applications based on whether the load is one-way or two-way. |
 View Bearing Type -Tapered Roller Bearings
View Bearing Type -Tapered Roller BearingsTapered roller bearings have widespread applications in various industries. They are commonly used in automotive applications such as wheel hubs, differentials, and transmissions. In the aerospace industry, they are employed in landing gear assemblies. Tapered roller bearings also find use in industrial machinery, including machine tools and conveyor systems. Additionally, they are crucial components in heavy equipment like construction machinery and mining equipment. These bearings excel at handling both radial and axial loads, making them essential for industries that require efficient load management and reliable operation.
Inner Diameter (d):
The inner diameter of a tapered roller bearing refers to the measurement of the inside diameter of the inner race.
Outer Diameter (D):
The outer diameter of a tapered roller bearing refers to the measurement of the outside diameter of the outer race.
Width (T):
The width of a tapered roller bearing refers to the measurement of the distance between the two races, including the rollers.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
|
(1). High Axial and Radial Load Capacity |
Tapered roller bearings are designed to withstand higher axial loads in addition to radial loads, making them versatile for various applications. |
|
(2). Thrust and Radial Load Bearings |
They can be used as both thrust bearings and radial load bearings due to their ability to handle axial forces in either direction. |
|
(3). Equal Axial Force Distribution |
When used in back-to-back pairs, tapered roller bearings distribute axial forces equally in either direction, ensuring balanced load bearing. |
Tapered Roller Bearings Size Chart 
 View Bearing Type -Rod End Bearings
View Bearing Type -Rod End BearingsRod end bearings have a threaded shank or a welding plate, allowing for easy installation and attachment to various mechanical systems. They are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial machinery. In automotive applications, rod end bearings can be found in steering linkages, suspension systems, and control arms. In aerospace, they are used in flight control systems and landing gear assemblies.
Inner Diameter (d):
The inner diameter of a tapered roller bearing refers to the measurement of the inside diameter of the inner race.
Outer Diameter (D):
In rod end bearings, the outer diameter typically refers to the diameter of the outer ring or housing.
Width (B):
Is the dimension across the widest part of the bearing's head.
Width (B1):
Refers to the measurement of the height of the ball within the bearing.
 View Bearing Type -Needle Roller Bearings
View Bearing Type -Needle Roller BearingsNeedle roller bearings find widespread applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, construction, and more. They are commonly used in automotive components like engines, transmissions, and drivetrain systems. In the aerospace sector, needle roller bearings are utilized in aircraft engines, landing gear mechanisms, and control systems. Industrial machinery, such as printing presses and textile machines, rely on these bearings for precise and smooth motion in limited spaces. Construction equipment, including excavators and bulldozers, also benefit from the durability and performance of needle roller bearings. Their compact size and high load-carrying capacity make them essential components in various industry applications.
Inner Diameter (dr):
The inner diameter refers to the size of the central hole or bore of the bearing.
Outer Diameter (D):
The outer diameter is the measurement of the bearing's outer ring.
Width (B):
The width, also known as the thickness, refers to the dimension between the inner and outer rings of the bearing.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
|
(1). High Load Capacity |
Due to the smaller diameter of needle roller bearings, more rollers can be installed in the same space, increasing the surface area in contact with the seat ring, enabling them to handle high loads effectively. |
|
(2). Space Efficiency |
Small sizes of needle roller bearings are useful in applications where space is limited, as they require a smaller gap between the shaft and the housing. |
Needle Roller Bearings Size Chart 
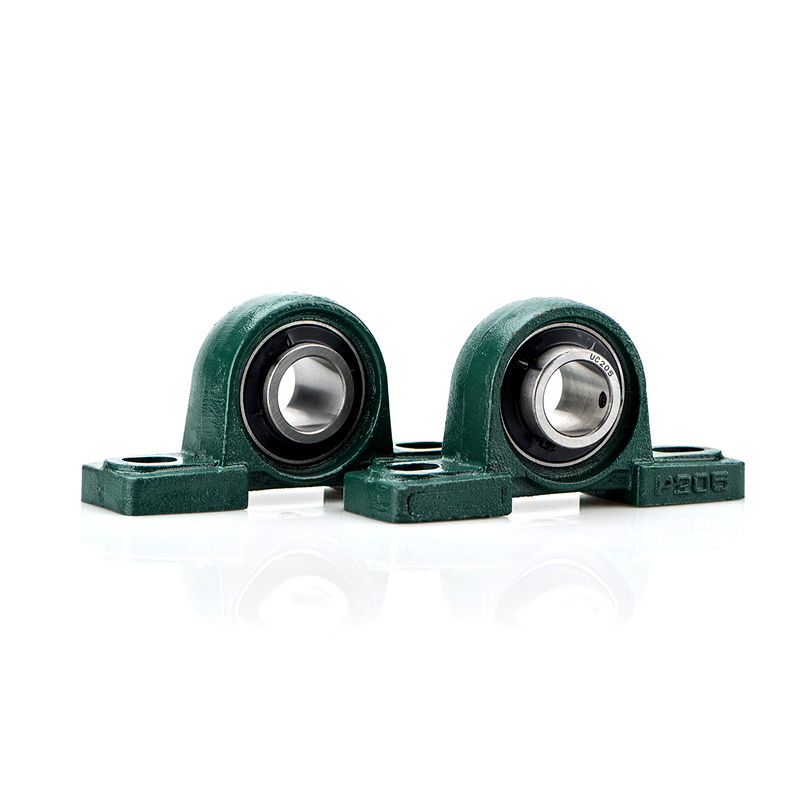

Pillow block bearings, also known as plummer block bearings, have a wide range of industrial applications. They are used in various industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, mining, construction, and specialized sectors like wastewater treatment and power generation. Pillow block bearings provide reliable support and smooth rotation for shafts in equipment such as conveyors, food processing machinery, packaging systems, agricultural machinery, mining equipment, and construction machinery. They are valued for their ability to handle heavy loads and ensure efficient operation. With their easy installation and maintenance, pillow block bearings are essential components in industrial settings that require reliable shaft support and smooth rotational movement.
Pillow Block Bearings Size Chart 
 Further reading:
Further reading:
Needle Bearing Size Chart|Teach you how to choose bearings correctly
Exploring the Versatility of Thin Section Bearings
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.