Need Support?
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.
ISK Bearings | B2B Bearing Wholesale

In industrial and mechanical applications, there are various <strong>bearing types</strong>, and their usage depends on specific applications and requirements. This article introduces six common types of bearings—deep groove ball bearings, tapered roller bearings, angular contact ball bearings, needle roller bearings, thrust ball bearings, and spherical roller bearings—and explains where they are typically used.
快速介紹
- It is one of the most widely used types of rolling bearings, and is very suitable for electric motors, gearboxes and household appliances.
- Designed for high-load applications, it can withstand radial and axial loads and is widely used in automotive wheels and heavy industrial equipment.
3.Angular Contact Ball Bearings
- It offers high precision and high-speed operation, making it particularly suitable for applications that require support for complex loads, such as machine tool spindles and turbochargers.
- Due to its compact design, it is suitable for applications with limited space and is commonly used in automotive drivetrains and light industrial equipment.
- Designed specifically to withstand unidirectional axial loads, it is commonly found in the structures of generators and turbines.
- It can automatically adjust for misalignment and withstand high loads, making it suitable for use in large industrial machinery and mining equipment.
⚠️The following bearing rankings do not imply a specific order, as each type of bearing has its unique advantages and suitable scenarios.
Deep groove ball bearings are super common and versatile. Thanks to their deep grooves, they can handle loads coming from different directions—whether it’s radial, axial, or both. They also run smoothly with low friction, even at high speeds.
You’ll often find these bearings in things like small electric motors, car transmissions, machine tool gearboxes, and other everyday machinery.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Types 
Tapered roller bearings are designed with an adjustable contact angle between the inner and outer rings, which helps them handle different load conditions. A larger contact angle generally means the bearing can take on more axial load. The clever design ensures the rollers make pure rolling contact by aligning their contact lines with a single point on the bearing axis.
You’ll typically find these bearings in car parts like wheel hubs, transmissions, and differential shafts. They’re also used in construction equipment, big agricultural machines, and gear systems in trains.
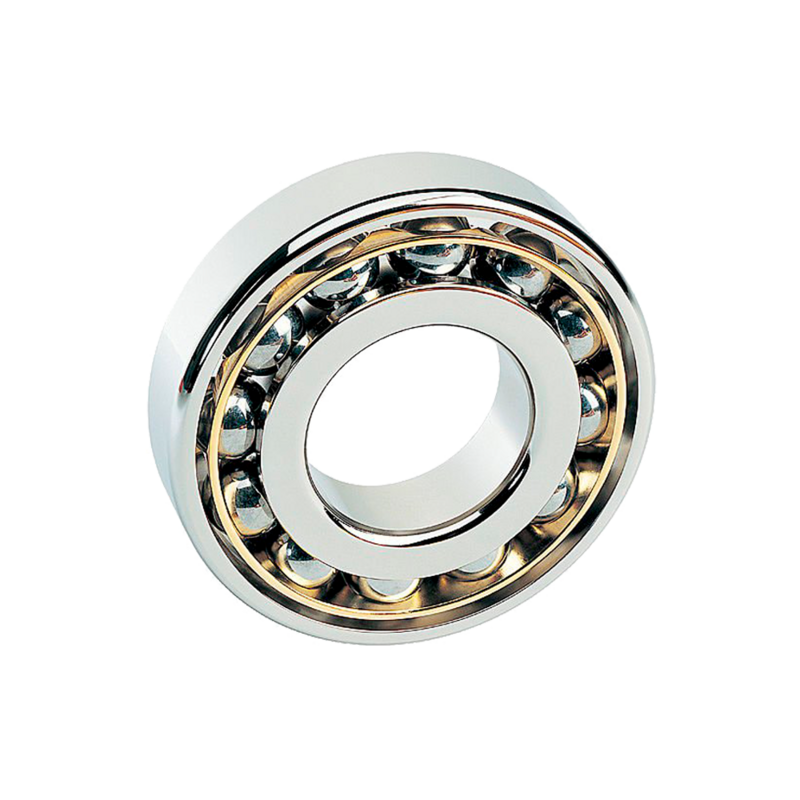

Angular contact ball bearings are built to handle both radial and axial loads at the same time, thanks to their inclined contact surfaces. Compared to deep groove ball bearings, they can take on higher axial loads.
The contact angle plays a key role here—it’s the angle between the line connecting the ball and raceway contact points and the vertical line to the bearing axis. Standard angles are 15°, 30°, and 40°. A larger contact angle means better axial load capacity, while a smaller one is ideal for high-speed performance.
You’ll often see these bearings in machine tool spindles, high-frequency motors, gas turbines, centrifugal separators, air compressors, fuel injection pumps, printing equipment, and differential gear shafts.
Needle roller bearings are designed for high-speed performance and stand out for their compact yet strong build. Their rollers are guided by a precisely engineered, rigid cage, which ensures minimal dimensional errors. Even with their smaller cross-section, they can handle heavy loads, making them ideal for setups where radial space is tight.
You’ll commonly find them in automotive engines, transmissions, pumps, excavator track rollers, overhead cranes, and compressors.
Thrust ball bearings are built to handle axial loads and consist of three key parts: the shaft washer (upper washer), the housing washer (lower washer), and a cage with steel balls. The shaft washer is usually slightly smaller in diameter than the housing washer, while the cage matches the size of the shaft washer. It’s important to remember that these bearings are designed exclusively for axial loads and aren’t suitable for radial loads.
They’re commonly used in automotive steering systems and machine tool spindles.
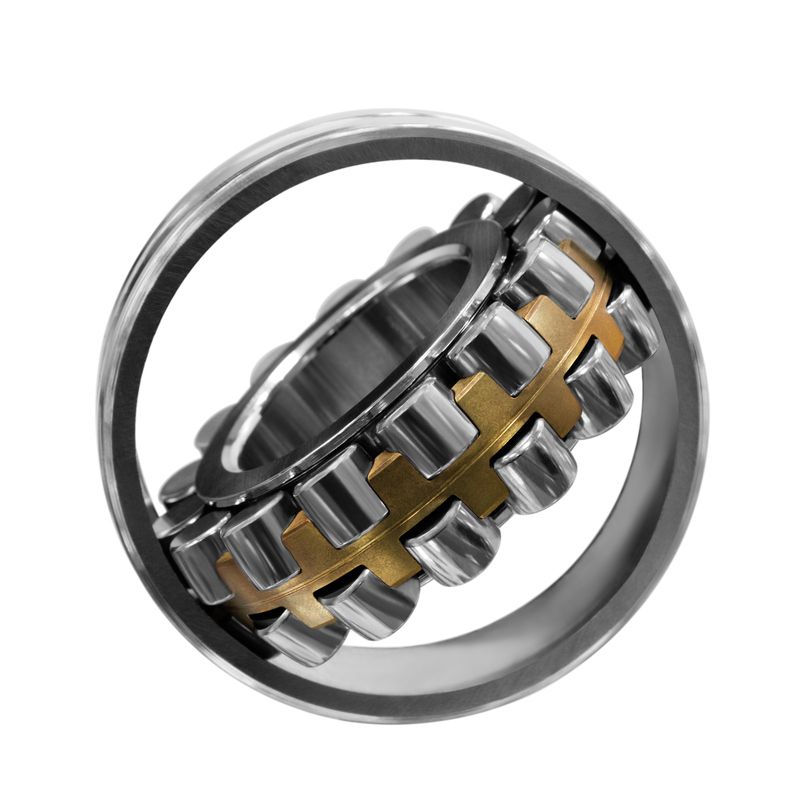

Spherical roller bearings have a unique self-aligning design, where the arc center of the outer race aligns with the bearing center. This feature lets the bearing automatically adjust to misalignment caused by shaft or housing deflection, maintaining proper axis alignment. These bearings are built to handle both radial and bidirectional axial loads, with exceptional performance under heavy radial and impact loads.
They’re widely used in applications like papermaking machinery, gear reducers, railway axles, printing presses, woodworking machines, and industrial gearboxes.
 Please Consult Our Team Directly
Please Consult Our Team Directly
These bearings represent some of the most commonly used types across various industries. In practice, multiple types of bearings are often combined to meet complex motion and load demands. Each industry and application comes with its own specific requirements, so selecting the right bearings means taking into account factors like load type, speed, precision, and operating environment.
 If you would like to explore additional types of bearings:
If you would like to explore additional types of bearings:
(1) Linear Bearings (aka Linear Motion Bearing): The Key Component for Precision Linear Motion
(2) Rod End Bearings: Key to Mechanical Connections
(4) Ceramic Bearing Specifications: Overview of Materials and Characteristics
 For more information on the application of industrial bearings, you may refer to:
For more information on the application of industrial bearings, you may refer to:
(1) Common Bearing Components in Electric Bicycles
(2) Choosing Durable Bicycle Bearings: A Guide to Ensuring Longevity and Performance
(3) The Future of Urban Delivery: The Revolution of Electric Cargo Bikes
 Further Reading:
Further Reading:
(1) Types of Bearings and Their Applications
(2) The introduction of bearing types
Bearing model numbers consist of three parts:
We previously helped an electromechanical equipment manufacturer in Asia resolve abnormal bearing noise issues. By optimizing the sealing structure and adjusting lubrication parameters, we significantly improved system stability and reduced maintenance costs.
Case reference: ISK BEARING Customer Cases
We offer a range of testing and technical services, including independent heat treatment, automated noise & vibration testing, clearance inspection, salt spray testing, and more — helping our clients improve product reliability and performance.
Resource overview: ISK Technical Resources
You can visit the ISK official FAQ section to explore answers related to bearing selection, product specifications, and more.
FAQ Section: ISK Bearings FAQ Center
As a bearing manufacturers, we have established an IATF16949-certified factory in Ningbo to ensure the highest quality of our products, which comply with RoHS, REACH, and SGS standards.
Discover more about the features and applications of various bearings.
Click here to explore more articles and find the perfect bearing for your project.
Needle Bearings (Roller Bearings) are a type of bearing that performs exceptionally well at high speeds. Their rollers are precisely guided by specially shaped, high-rigidity cages with minimal dimensional error. Despite their small cross-section, needle bearings...
How Do Ball Bearings Work? Bearings are often small and unassuming components in a product, yet they are crucial for its proper functioning. Without bearings, many products would fail to operate effectively. But do you know how ball bearings...
Please provide your question. We’ll find you with the best support options.